Eliminating static charge from molds
Eliminating static charge from molds after resin molding
You wish to eliminate the static charge from molds after resin molding since any remaining charge will cause resin to remain in the mold, which can damage the mold, cause defective parts to proceed to the next process, or result in brief production line stoppages.
[Issue] Ionizer’s operating temperature range
You wish to eliminate charge using an ionizer, but the mold remains hot immediately after molding, causing the ambient temperature to exceed 60°C 140°F and precluding use of a standard ionizer.- Molded parts remain in the mold, damaging it.
- Defective parts proceed to the next process.

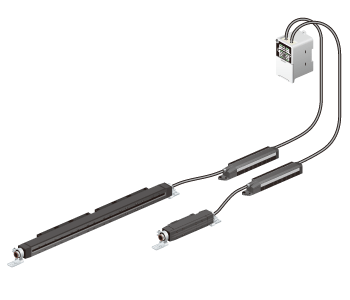
[Solution] Eliminate charge using a heat-resistant model of the ER-X Ionizer (ER-X□HC).
Install an ER-X□HC Ionizer with a compact, heat- and cold-resistant bar head (head operating ambient temperature: -60 to +200°C -76 to +392°F) near the mold to eliminate charge.

Charge elimination efficiency
By connecting two heads to a single controller, you can boost charge elimination efficiency.
Key considerations in choosing a sensor
Environmental resistance
With an operating ambient temperature of -60 to +200°C -76 to +392°F, the product can eliminate charge in hot equipment like molding machines.
Space-saving design
Thanks to a super-compact head design (30 mm × 22 mm 1.181 in × 0.866 in), the product can be installed in confined spaces.
Airless charge elimination
The product can also be used in airless charge elimination applications, ensuring that moving air won’t lower the temperature of the mold or scatter resin.
Related information
Related articles
-
Measuring the dimensions of a snap-fit mechanism
Measuring the dimensions of a snap-fit mechanism
-
Testing for distortion in die-cast parts
Measuring distortion in die-cast parts with a contact-type sensor
-
Measuring the thickness of metal parts (speaker center caps)
Detecting overlapping metal speaker parts (center caps)
-
Measuring the inside diameter of a motor core (eccentricity testing)
Measuring the inside diameter of a motor core and testing eccentricity
-
Measuring the height of circuit boards during assembly
Detecting circuit board location in an automatic assembly process
-
Measuring misalignment of rolled metal sheets
Detecting overlapping metal speaker parts (center caps)
-
Implementing remote monitoring of equipment and a paperless workflow for daily reports
Implementing remote monitoring of equipment and a paperless workflow for daily reports
-
Assessing the overall safety status of equipment at a glance
Assessing whether multiple equipment doors are open or closed at a glance







