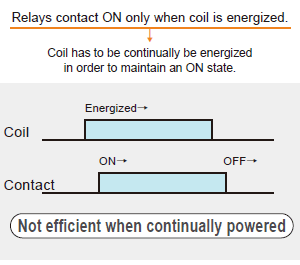
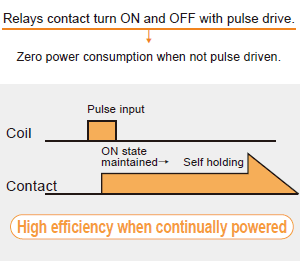
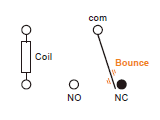
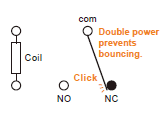
- Home
-
Products
- Components & Devices
-
FA Sensors & Components
- General-purpose Sensors
- Machine Vision System
- Displacement Sensors
- Safety Components
- Static Control Devices
- Programmable Controllers
- Laser Markers
- Human Machine Interface
- Others
-
Motors for FA & Industrial Application
- Motors for FA
- Download
- Resource
-
Support
- Technical / Sales Support
- Service / Support
-
Sales Locations
- Sales & Support
- Global Support
- Home
-
Products
- FA Sensors & Components
- Machine Vision System
- Displacement Sensors
- Safety Components
- Static Control Devices
- Programmable Controllers
- Laser Markers
- Human Machine Interface
- Others
- Download
- Resource
-
Support
- Technical / Sales Support
-
Sales Locations
- Sales & Support
- Global Support
Panasonic Industry / Automation Controls